You are here: Foswiki>Andypublic Web>MyBlog>BlogSeptember2002>InfluenzaPandemic (26 Apr 2009, andyp)Edit Attach
An Influenza Pandemic is probably the thing which will kill you. OK, I haven't done the full stats, but it's pretty likely...
There's a Momus song called Morality is Vanity which goes
Seven million people died in the great war,
a bout of influenza quadrupled that score.
Why pimp to posterity?
Why should they admire us?
All the heroes of Valhalla
Weigh less than a virus.
(Full lyrics at http://www.phespirit.info/momus/19900101.htm )
This section has been written and researched by Andy Pryke, and I would be grateful if you contacted me before duplicating or publishing it - thanks!
Seven million people died in the great war,
a bout of influenza quadrupled that score.
Why pimp to posterity?
Why should they admire us?
All the heroes of Valhalla
Weigh less than a virus.
(Full lyrics at http://www.phespirit.info/momus/19900101.htm )
"Bird Flu" Deaths (Avian Influenza)
The 1997 Hong Kong "Chicken Flu" killed 6 of the 18 people who caught it. On 10th October 2005, the WHO issued figures for the H 5 N 1 strain. The total number of cases was 117, and the total number of deaths so far 60. This gives a mortality rate of around 52%. WHO figures at: http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/country/en/| WHO figures | H5N1 infections | Deaths | % Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|
| January - March 2004 | 35 | 24 | 69% |
| August - October 2004 | 9 | 8 | 89% |
| Dec' 2004 - 10th October 2005 | 86 | 35 | 40% |
| Total Jan 2004 - 17th November 2005 | 130 | 67 | 51% |
How many people could die in a UK outbreak?
The UK influenza contingency plan (website) assumes a mortality rate of 0.37% for planning purposes. Yep. That's not a typo, nought point three seven percent. That's around 140 times lower than the observed figure of 51%. The table below gives figures ased on a UK population of ~58Million, the WHO estimate of an infection rate of 25% (14.5 million people) and the current mortality rate of 51%, you get around 7.4 million UK deaths.| Mortality rate | No. UK Deaths | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 0.37% | 54k | The scenario the UK contingency plan uses |
| 1.00% | 150k | |
| 2.50% | 360k | Estimated death rate of the 1918 pandemic |
| 5.1% | 740k | One tenth of the reported death rate |
| 25.00% | 3.6 million | |
| 51.00% | 7.4 million | The current mortality rate (November 2005) |
| 62.50% | 9.0 million | The mortality rate in April 2005 |
What is a Pandemic
According to [7], an influenza pandemic is an outbreak which spreads throughout the world, has a high infection rate and is caused by a new strain.Previous Pandemics, Epidemics and Outbreaks
- Pandemic Mortality, 1700 to Present Day [7]:
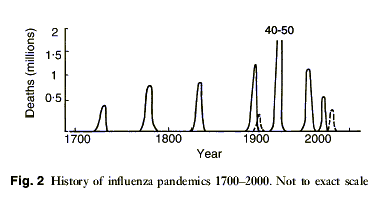
| Year | Event | Deaths | Mortality | Strain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| "412 BC": | Many papers and websites report that Hippocrates documents an influenza epidemic in 412, but I have been unable to find references. My guess is that many of these have just copied the info without checking, but that the original reference is to "the Cough of Perinthus" in book IV in the book "Of the Epidemics" | |||
| 212 BC | In hot Autumn weather, the Roman army is besieging Achradina, when "both sides were visited by pestilence, a calamity almost heavy enough to turn them from all thoughts of war." Livy's Account (external site) Those tending to the ill also caught the disease, and eventually funerals traditions were abandoned, and the dead left where they were. | |||
| 855 | "Ebn-al-Atir mentions a virulent epidemic resembling influenza that started in Central Asia in 855-856 and spread across Persia... killing a large number of people (Ebn al-Atir, Beirut, VII, p. 80)." [6] | |||
| 1510 | Large scale outbreak, probably pandemic [7]. Perhaps originating in Africa, it raged across Europe | |||
| 1557 | "Large scale outbreak" | |||
| 1580 | Pandemic. The first outbreak which is generally accepted as pandemic [7]. Originating in the North Africa during summer, it spread to Sicily, then up through Italy, through Europe and to North America. In some Spanish cities nearly everyone perished. [2][4] | |||
| 1688, 1693, 1699 | Outbreaks in England, Ireland and America. High infection rates are reported from the 1699 strain in Massachusetts[4] | |||
| 1729 -33 | Pandemic. Reported as originating in Russia in April 1729, it lay low over the summer and re-emerged in Sweden in September, Vienna in October. In November it spread across Europe, not reaching the Americas till 1732. Deaths were "most numerous amongst the elderly and pregnant women", and later waves were more severe [2][1] | "Relatively low Mortality" | ||
| 1781-2 | Pandemic. The first wave started in North Africa and North America in 1781. A pandemic wave started China the next year, and swept across Europe and the Americas during the summer. Two thirds of the population of Rome became ill (7). 10's of millions were infected [2] | |||
| 1789 | Epidemic in USA and Europe. | |||
| 1830-33 | Pandemic. Spreading out from China, waves hit in 1830-31 and re-occur in 1832-33. The infection rate is high(20-25%), but mortality low | |||
| 1836-37 | (unclear) | |||
| 1847-48 | Epidemic. Outbreak in London (and elsewhere??) | |||
| 1889-1890 | Pandemic. Originating in central Asia, it followed a familiar path through Russia and Europe. The first wave was relatively mild, with low mortality, the subsequent three waves were more severe. Reports from Iran identifies high mortality amongst children, and infection rates of up to 50% [1][5] | ~1m | H 2 N 2 | |
| 1900: | Pandemic / Major epidemic. As excess mortality is only reported in North America, England and Wales, not all experts agree this counts as a pandemic[9]. | H 3 N 2 | ||
| 1918-1920: | Pandemic. The "Spanish flu" kills 50 to 100 million people, equivalent to 175-350m given today's population[4]. As noted in the Momus quote above, it kills more people than World War I. Movements of US and other troops help spread the virus. It is thought to have originated in the United States in Feb 1918[8], or perhaps a year earlier in France. The second wave (Autumn 1918) was much more lethal, with unusually high mortality rates especially among young, otherwise healthy adults (see graph). This may have been due to an over enthusiastic immune response damaging the lungs[3]. Symptoms include "the most vicious type of pneumonia". Within a few hours Cyanosis has appeared, and after another few, death. | 50m - 100m [4] | 2.5% + | H 1 N 1 |
| 1957-58: | Pandemic. "The Asian Flu" originated in China in February 1957, it spread across the globe in 6 months. A second wave emerged across multiple countries in early 1958, with differing severity by region. About 40-50% of people were infected, and 25% to 30% experienced symptoms. [7] | > 1m | H 2 N 2 [3] | |
| 1968-69 | Pandemic. "The Hong Kong Flu". Strangely, figures given for this epidemic range from 100k [10] to 1m-4m. WHO figures seems to be about the 1million mark | ~1m | H 3 N 2 | |
| 1976: | A outbreak of a Swine related strain of flu at Fort Dix in February lead to plans for a massive vaccination program in the USA. Over 40 million people were vaccinated, starting in October. The program was suspended on the 16th of December following reports of Guillain-Barr\xE9 Syndrome (GBS) in recipients. By January 1977, over 500 cases of GBS were reported, with 25 deaths.[11]. | H 1 N 1 | ||
| 1977 | Pandemic. "Russian Flu" was first detected in November 1977, and spread across Siberia and European part of Russia.[9] There are suggestions that this wasn't a natural outbreak but an escape of a laboratory strain[1]. | "No Excess Mortality"[1] | H 1 N 1 |
- Mortality by age 1892 and 1918[1]:
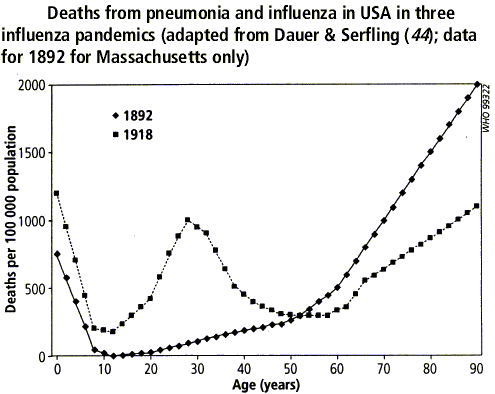
- Mortality by age 1958 and 1969[1]:
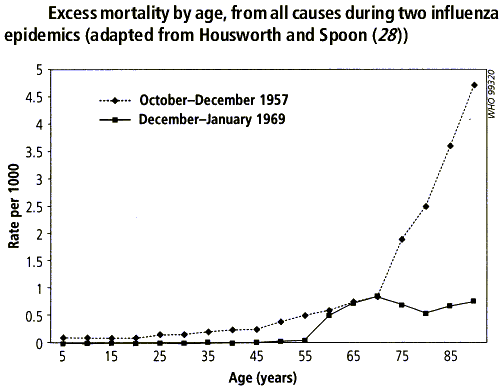
References
[1] Dowdle WR., Influenza A virus recycling revisited. Bull World Health Organ. 1999;77(10):820-8. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/bulletin/1999/Vol77-No10/bulletin_1999_77(10)_820-828.pdf [2] Nice overview with historical and medical info - http://www.medicalecology.org/diseases/influenza/influenza.htm#sect2.2 [3] http://www.cidrap.umn.edu/cidrap/content/influenza/panflu/biofacts/panflu.html [4] The Threat of Pandemic Influenza: Are We Ready? Workshop Summary (2005) - http://www.nap.edu/openbook/0309095042/html/57.html http://www.na[/0309095042/html/68.html [5] http://www.portfolio.mvm.ed.ac.uk/studentwebs/session2/group21/1889.htm [6] Influenza in Iran - http://www.iranica.com/articles/supp4/Influenza.html [7] C.W.Potter, A History of Influenza, Journal of Applied Microbiology Volume 91 Iss[ October 2001 - http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/links/doi/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01492.x/pdf [8] John M Barry, The site of origin of the 1918 influenza pandemic and its public health implications, Journal of Translational Medicine 2004, 2:3,doi:10.1186/1479-5876-2-3 - http://www.translational-medicine.com/content/2/1/3 [9] Alan W. Hampson, Surveillance for Pandemic Influenza, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Volume 176 S1, August 1997 - http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/JID/journal/issues/v176nS1/au03_8/au03_8.web.pdf [10] http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/CID/journal/issues/v33n8/001674/001674.text.html#rf1 [11] Elissa A. Laitin and Elise M. Pelletier, The Influenza A/New Jersey (Swine Flu) Vaccine and Guillain-Barr\xE9 Syndrome: The Arguments for a Causal Association, Drugs and Devices Information Line, 1997 - http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/Organizations/DDIL/swineflu.htmlWeb Links
- Good "home medical" overview %EXT%, including some alternative medicine treatments
- A doctor's description of an outbreak of the 1918 pandemic %EXT%at a U.S. army base
- Timeline of the 1918 Epidemic %EXT% in the USA
- Overview of how flu works and spreads + how outbreaks and pandemics are dealt with %EXT% (CDC / National Vaccine Program Office)
- The history of influenza pandemics %EXT%
- A chronology of epidemics %EXT% (from 480 BC onwards), with interesting
- Chronology of epidemics - http://www.immunize.cpha.ca/english/consumer/student/whatflu/epidem.htm
- Yin Qiao San / Yin Qiao Jie Du Pian - Chinese Herbal Medicine for Influenza %EXT%
- Rather off the wall theory that Influenza is from Venus %EXT%(presumably Typhus is from Mars)
| I | Attachment | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
mortality_by_age_1892_1918.gif | manage | 13 K | 23 Mar 2005 - 00:39 | Unknown User | Mortality by age 1892 and 1918. |
| |
mortality_by_age_1957_1969.gif | manage | 10 K | 23 Mar 2005 - 00:40 | Unknown User | Mortality by age 1958 and 1969 |
| |
pandemic_mortality_1700_to_present.gif | manage | 5 K | 23 Mar 2005 - 00:38 | Unknown User | Pandemic Mortality, 1700 to Present Day |
Edit | Attach | Print version | History: r12 < r11 < r10 < r9 | Backlinks | View wiki text | Edit wiki text | More topic actions
Topic revision: r12 - 26 Apr 2009, andyp
Favourite Pages
My Blog
Best Of Blog 2007
Best Of Blog 2005 Birmingham,
How to be Happy,
Influenza Pandemic,
Moseley Tornado,
Misty's Big Adventure,
Street Furniture Stickers,
Weird Internet Animations
Other People's Blogs
Birmingham Bloggers Danger! High Postage,
Parallax View,
Pete Ashton,
Silent Words Speak Loudest
Please don't ask for a sidebar link as a refusal often offends. Editorial Policy
My Blog
Best Of Blog 2007
Best Of Blog 2005 Birmingham,
How to be Happy,
Influenza Pandemic,
Moseley Tornado,
Misty's Big Adventure,
Street Furniture Stickers,
Weird Internet Animations
Other People's Blogs
Birmingham Bloggers Danger! High Postage,
Parallax View,
Pete Ashton,
Silent Words Speak Loudest
Please don't ask for a sidebar link as a refusal often offends. Editorial Policy
 Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors. Ideas, requests, problems regarding Foswiki? Send feedback


